Industrial electrical systems are complex. They power machines, processes, and vital safety infrastructure across many types of facilities.
For this reason, proper maintenance is not optional; it’s a must. It is essential, most important, the safety. Additionally, it ensures the stability and long-term reliability of the equipment.
Poor maintenance can cause downtime. It can damage equipment. In severe cases, it can injure workers. Many common failures originate from simple issues.
These failures include dirty panels, loose terminals, and aging components. The routine inspection and proper documentation always help to early detect these issues.
Clear procedures help technicians work safely. Continuous training strengthens maintenance culture and prevents mistakes.
The following tips support reliable electrical operation. They address practical actions used in most industrial environments. They reduce risks, extend equipment life, and improve system availability.
This article reviews essential maintenance practices. It also discusses their impact on industrial electrical reliability.
Follow a Preventive Maintenance Schedule
Every industrial facility must have a well-structured preventive maintenance schedule. It will be followed during the maintenance time.
This method is always clear, consistent, and aligned with equipment manufacturer recommendations.
By addressing wear before it becomes critical, preventive tasks reduce failures. They help keep electrical systems stable under different operating conditions. Recording dates and findings is essential.
This must be done for each maintenance activity because it helps identify trends, repeated issues, and devices that may be approaching the end of their expected service life.
Perform Routine Visual Inspections
Routine visual inspections are one of the simplest. There are several effective ways to catch early signs of trouble. This is because they reveal issues long before they cause system failures.
Check for missing labels and signs of wear on components during the inspection. Additionally, look for signs of wear such as cracked insulation, loose glands, or discolored cables during the inspection.
These minor symptoms often point to larger hidden problems. Although visual checks do not replace deeper diagnostic tests, they should be performed daily to prevent unexpected downtime.
Tighten Electrical Connections Periodically
In any industrial environment, loose electrical connections are extremely common. This is due to dust, vibration, heat cycles, and general mechanical stress.
As terminals loosen, contact resistance increases. The outcome is the generation of heat that escalates over time.
Such heat can eventually burn wires or damage breakers. To prevent this, verify torque values regularly, use the correct tightening tools, and always follow manufacturer specifications.
Clean Electrical Panels Regularly
Just like any electrical device or component, dust and airborne contaminants usually accumulate inside electrical panels.
This buildup can reduce equipment lifespan because of the creation of conductive paths and the promotion of corrosion.
Additionally, the accumulation of moisture can exacerbate the problem. In environments with cutting fluids or oil mist, contamination becomes even worse because sticky residue traps additional particles.
Panels should be cleaned regularly using appropriate tools and methods that avoid forcing debris into sensitive components.
Inspect Cooling and Ventilation Systems
Electrical devices such as PLCs, VFDs, or contactors always generate heat. Fan filters become clogged, and heat sinks quickly accumulate dust.
These dusts tend to restrict airflow. This can lead to overheating, which, as a result, causes premature failure.
It is very important to regularly check ventilation paths and replace filters. In addition, confirm fan operation and measure enclosure temperatures. Also ensure the panel door is properly closed after maintenance.
Check Cable Routing and Support
Cables usually can sag and rub against sharp edges. Furthermore, when not properly supported, they can rest on hot surfaces.
Such conditions can shorten cable life due to the creation of hazards. Proper is a good practice because it keeps cables organized, prevents interference, and reduces mechanical stress.
Plus, the minimum bending radius must be respected. Clear labeling of cables is not an option.
Also, separate power cables from control or signal lines to reduce electrical noise and improve troubleshooting.
Verify Protective Devices Regularly
Protective devices such as overload units and breakers must function correctly at all times.
Without forgetting relays, they age, drift, or wear mechanically. Regular testing ensures they react properly under fault conditions.
Always simulate fault scenarios when possible. Thereafter, verify trip curves and inspect moving parts for damage or contamination. Faulty protection can cause catastrophic equipment damage increases the downtime.
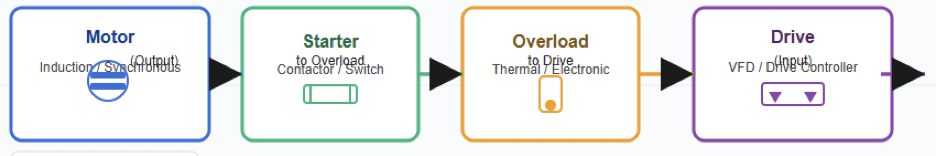
Maintain Motor Starters and Drives
Motors drive most industrial processes, so their starters and drives must be kept in good condition.
Inspect contactor tips for pitting, verify overload settings, clean VFDs, document fault histories, and listen for unusual motor sounds.
Monitoring motor current can also reveal imbalances or developing mechanical problems.
Consistent maintenance helps prevent sudden motor failures that can stop an entire production line.
The figure below indicates a block diagram of a combination of motor—starter-overload and drive.
Thermal Imaging for Hot Spot Detection
Thermal imaging provides fast and accurate detection of overheating components that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
To mention a few, hot spots often indicate loose terminals, overloaded cables, or failing equipment.
Capture thermal images during normal operating conditions. Then compare them over time to track deteriorations. Prompt repairs prevent failures and improve overall system safety.
Test Insulation Resistance
It is known that insulation gradually degrades the different reasons. It could be heat, moisture, contamination, or age. Using an insulation resistance tester annually is an effective way to assess cable and motor health.
Make sure a measured resistance shows a significant drop. This indicates deterioration and the need for replacement. Having strong insulation protects equipment from severe damage because it prevents short circuits.
Proper Grounding and Bonding
A well-connected grounding stabilizes voltage. It also protects equipment and prevents dangerous shock hazards.
Noise can be introduced to the electrical system if loose grounding connections are used. This will increase the risk of fault currents.
Inspect grounding bars, tighten all lugs, measure grounding resistance when possible, and ensure all enclosures are properly bonded. Effective bonding practices support safe and stable operation.
Check Power Quality Regularly
Poor power quality affects sensitive equipment. This causes overheating and leads to erratic behavior in control systems such as PLCs and VFDs. Measure harmonics, voltage imbalance, and power factor to assess system health.
Power quality trends should be recorded over time. This helps to identify and resolve issues with voltage regulators, using filters or improved cable separation. The next figure shows the power quality waveform (Pure sinusoidal in blue vs distorted one in red).
Lubricate Mechanical Components Inside Switchgear
For proper operation, switchgear contains mechanical parts that should move freely. If old grease is used, it restricts movement due to the hardening effect. Slow or sticky mechanisms can delay breaker operation. This method is unsafe during faults.
The correct lubricant must be applied as recommended by the manufacturer. Also, the use of unsuitable alternatives must be avoided because they may damage the equipment.
Replace Aging Components Before They Fail
All electronics and electrical components have a limited lifespan. Contactors wear out, and capacitors dry out.
In addition, relays tend to drift out of tolerance. Replacement cycles must be established based on operating conditions.
Also, data, such as historical failures and manufacturer guidance, must be considered. Components must be replaced before they fail. This helps to avoid dealing with unexpected breakdowns.
Keep Spare Parts Organized
A well-managed spare parts system reduces repair times because technicians can access the correct components quickly.
Label all parts, store everything in clean, dry conditions, and track inventory. Electronics can age even when unused, so review expiration dates and update the inventory list regularly.
Document Every Repair and Modification
Accurate documentation supports faster troubleshooting and safer maintenance. Update wiring diagrams, note any cable or configuration changes, record drive parameters, and document torque values and fault codes. Poor or missing documentation often leads to mistakes and increases repair time.
Ensure Proper Tagout/Lockout Procedures
To prevent accidental energization, lockout and tagout are a must. It prevents the circuit from being energized during maintenance. This is essential for protecting workers from severe injuries.
Always isolate the equipment, apply locks, place tags, and verify zero energy before starting work. Inspect LOTO devices regularly and train personnel frequently to maintain safety awareness.
Train Personnel Regularly
Training ensures workers maintain essential knowledge. New technologies must be introduced to the plant and the team in general. The training sessions should be attended as often as possible per year.
Including hands-on practice is a good idea if possible. In addition, provide updates on diagnostic techniques.
Do not forget to include testing tools and new standards. Safety and efficiency are a result of a well-trained team.
Pay Attention to Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors such as chemical fumes, heat, humidity, and dust can severely affect electrical equipment.
Degrading of insulation, corrosion, and the blocking of insulation can be extended by the poor environment.
Regularly review the conditions, enhance enclosure ratings, add filters, install cooling systems, or reduce vibration as necessary to extend the life of the equipment.
Implement Remote Monitoring Where Possible
Now that we are in the IIoT era, remote monitoring enhances reliability by detecting early signs of failure.
Sensors that track vibration, temperature, and current can reveal abnormal patterns. This helps prevent abnormalities before a breakdown occurs.
Modern IoT and wireless systems make installation easier and provide continuous data for analysis and maintenance planning.
Calibrate Meters and Instruments
Components such as relays tend to drift over time. Test them; if they provide for inaccurate readings can lead to incorrect maintenance decisions.
Calibrate current clamps and voltage meters. Additionally, other diagnostic tools should be calibrated at least once a year. The calibration must be done by following standardized procedures to ensure measurement accuracy.
Review Safety Codes and Standards
NFPA, IEC, and OSHA are the safety codes that change over time. Their compliance is essential to protect workers and equipment.
Updates must be reviewed regularly, and procedures must be followed. Furthermore, incorporate new requirements into your maintenance practices.
Avoid Overloading Circuits
Electrical loads, especially nonlinear loads, often increase as facilities grow. The circuits can become overloaded without clear planning.
Current levels must be measured and compared with breaker ratings. In addition, evaluate peak demand.
This data will be used to appropriately size conductors to prevent overheating and nuisance trips.
Improve Panel Labeling
Clear and durable labels make maintenance safer and faster by reducing confusion during troubleshooting.
Use consistent labeling standards, include color codes for different voltage levels, and label wires, terminal blocks, and devices on both ends.
Work Areas Clean and Accessible
As mentioned above, a clean and organized work area reduces maintenance time. They also minimize risks.
Maintain adequate clearance around panels and keep tools organized; there is no option. Then ensure floors remain clean. Effective housekeeping supports safer and more efficient electrical work.
Periodic System Upgrades
Industrial systems age, so use only up-to-date components that meet safety and performance requirements. Upgrade old panels and replace worn relays.
Furthermore, installing modern breakers and updating sensors to improve reliability is recommended. This helps to reduce long-term risk, among others.
Good Wiring Techniques
Good wiring practices improve airflow. It simplifies noise and, most importantly, reduces electrical troubleshooting.
Use ferrules, select the correct wire size, and separate AC, DC, and signal cables to avoid interference and maintain system organization.
Use Surge Protection
Lightning and surges can always damage sensitive (control) electronics. Surge protection devices are designed for this purpose.
Drives, HMIs, and PLCs must have these kinds of protections. Then, if a major surge event occurs, the modules must be replaced to maintain effectiveness
Record Motor and Load Trends
Track motor current, temperature, and vibration or noise. If this is done over time, it helps identify electrical as well as mechanical issues before they become serious. Trend analysis typically tracks predictive maintenance.
vention
Not only are technical skills important, but workplace factors also play a huge role in achieving maintenance perfection.
If supervisors enforce procedures, this will help workers’ assurance about the equipment. Furthermore, management must support continuous improvement. A preventive mindset reduces failures and strengthens overall reliability.
Conclusion
This article reviewed key electrical maintenance practices used in industrial facilities. From the above, we could see that maintenance requires discipline and consistency.
Also, it needs planning and careful execution to keep equipment operating safely and reliably.
Small improvements such as cleaner panels, tightened terminals, and proper grounding can prevent major failures.
The article also detailed that strong documentation helps every technician while training. Additionally, during remote monitoring, it is important to provide ongoing support and early warnings.
With preventive maintenance, the downtime can be reduced and worker safety can be worker safety can be increased, and the equipment can be maintained.
We should not assume that an electrical system will remain reliable on its own. Skilled people/engineers or technicians must be present.
To ensure a safe approach, these personnel must receive additional training. Equipment life increases when these practices are applied consistently. In addition, failure rates drop, and overall operational efficiency improves.
FAQ: Industrial Electrical Maintenance Tips
Why is electrical maintenance important?
It prevents failures, reduces downtime, and improves safety.
What tasks are part of routine maintenance?
Routine maintenance tasks include inspection, cleaning, tightening terminals, testing protection devices, and checking insulation.
How often should maintenance be done?
Maintenance should be performed every 3–6 months, depending on the load and environmental conditions.
What safety rules should be followed?
Use LOTO, wear PPE, and work only on de-energized equipment.
What is better: preventive or predictive maintenance?
Both. Preventive is scheduled; predictive relies on condition monitoring.
What tools are essential?
Multimeter, insulation tester, infrared camera, and insulated hand tools.
Why is documentation important?
It helps track issues, plan maintenance, and improve troubleshooting.
What happens if maintenance is ignored?
Ignoring maintenance leads to more breakdowns, higher risks, and shorter equipment life.
Do environmental conditions matter?
Yes. Dust, heat, moisture, and vibration require more frequent checks.
Do technicians need special training?
Yes. Proper training ensures safe and correct maintenance work.