A toggle switch is a fundamental electrical component. It features a mechanical lever or handle.
This lever moves back and forth to control an electrical circuit. Toggle switches are used in many diverse applications.
These range from simple household lighting to complex aerospace control panels. Their primary function is reliable circuit control. Understanding their various types is important for proper application.
This guide explores the main classifications of these versatile devices. We will cover classifications based on their internal contacts and mechanical actions.
Classification by Poles and Throws
Toggle switches are often classified by “poles” and “throws”. A pole is the number of separate circuits the switch controls. A throw is the number of positions each pole can connect to. Functionality of every toggle switch is usually defined by this terminology.
Single Pole Single Throw
They simplest known as SPST. These are the simplest type. It controls just one circuit. It has an input terminal, and another one is an output terminal. It contains only two states, the ON state or the OFF state. When ON, the circuit is closed, allowing current flow.
When OFF, the circuit is open, stopping current flow. Common household light switches are often SPST.
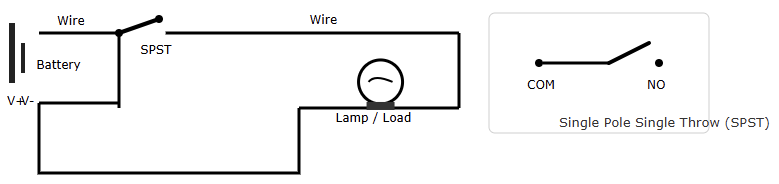
Single Pole Double Throw
In short, they are called SPDT. This type of switch contains two output options. Nevertheless, it is designed to control only one circuit. It has three terminals in total. It connects the single input to one of two possible outputs. The switch toggles between these two connections.
This is a changeover switch. It is useful for switching a single power source between two different devices.
Switching the headlights of the car from low beams to high beams is a vivid example of this kind.
Double Pole Single Throw
In short, they are mentioned as DPST. Two separates simultaneously circuits can be controlled by a DPST.
It operates like two synchronized SPST switches. Two inputs and two outputs are the terminals contained in DPST. It has a single ON or OFF position for both circuits at the same time.
This type is used when both the live and neutral wires of an AC circuit need to be disconnected for safety. Industrial equipment often uses DPST switches.
Double Pole Double Throw
Also known as DPDT. The high versatility is an important characteristic of the DPDT. It controls two independent circuits.
Each circuit can be connected to one of two outputs. It functions like two synchronized SPDT switches. A DPDT switch has six terminals in total.
A common application is reversing the direction of a DC motor.
Classification by Mechanical Action
The way a toggle switch behaves when actuated is another key classification. This is determined by its mechanical action. There are two primary action types: maintained and momentary.
Maintained Contact Switches
Maintained switches stay in the position to which they are moved. They have a latching mechanism. They remain in that state until manually moved again. A standard wall light switch is a perfect example.
Once flipped ON, it stays ON. Once flipped OFF, it stays OFF. These are used for applications requiring a continuous, steady state.
Momentary Contact Switches
Momentary switches only remain active as long as the actuator is held in position. They use a spring mechanism to return to their default state upon release. A doorbell button is a classic example. The bell rings only while the button is pressed. They are used for temporary actions or sending a brief signal.
Specialized Toggle Switch Types
There is an existence of a large number of specialized toggle switches. They are different from basic functionality toggle switches. They are designed for specific environments or user needs.
Illuminated Toggle Switches
The built-in light, usually an LED in the actuator, is contained in these kinds of switches.
The function of the aforementioned light is to indicate the current status of the switch.
This means either it is ON or OFF. This feature enhances visibility in low-light conditions. Control panels and automotive dashboards make very important use of them.
Sealed Toggle Switches
The kind of switches are also known as environmentally sealed switches. This is because they are built for harsh conditions. They have protective coatings and feature seals. This characteristic helps to resist chemicals, moisture, and dust.
They often have an IP rating, such as IP67, which indicates high protection. These are common in marine, military, and off-highway vehicle applications.
Locking Toggle Switches
Locking toggle switches have a mechanism that prevents accidental operation. The user must perform an extra action, like pulling the lever outwards, before toggling it. This adds a layer of safety. They are used in critical or high-risk industrial environments.
Conclusion
This article detailed about different types of toggle switches. We were able to see that toggle switches are essential components in countless systems. Their types vary widely based on circuit needs and operating environment.
Classifying them by poles/throws (SPST, SPDT, DPST, DPDT) defines their electrical function. Distinguishing between momentary and maintained action defines their physical operation.
Specialized types offer solutions for unique challenges. This could refer to very harsh environments and lighting conditions. Safety is ensured if the right selection is made. This provides the reliability and proper functionality for any application.
FAQ: Types of Toggle Switches
What are the main circuit types of toggle switches?
The most common types are SPST, SPDT, DPST, and DPDT, which refer to how many circuits the switch can control and how many connection paths it has.
What does SPST mean?
SPST (Single Pole Single Throw) is the simplest toggle switch, with basic ON/OFF control of one circuit.
What does SPDT mean?
SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw) can connect one circuit to either of two outputs, useful for selecting between two circuits.
What does DPST mean?
DPST (Double Pole Single Throw) switches two separate circuits on or off at the same time.
What does DPDT mean?
DPDT (Double Pole Double Throw) can switch two circuits and choose between two positions for each, and is often used for reversing motors or complex controls.
What is a momentary toggle switch?
A momentary toggle switch only stays in the active position while held; it returns to its default when released.
What’s the difference between maintained and momentary action?
Maintained stays where it’s switched; momentary returns when released.
Are there special styles of toggle switches?
Yes, locking, illuminated, miniature, and sealed toggle switches exist for safety, visibility, space constraints, or harsh environments.
How do you choose the right type?
Pick based on how many circuits you need to control, whether you need ON/OFF or changeover, and whether the switch should stay in position or be momentary.
Can toggle switches be used in high-temperature or industrial settings?
Yes, some are built for rugged, high-heat, or harsh environments with special materials and seals.