In the modern world, industrial automation and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) play a critical role.
Their main applications are controlling machines, manufacturing lines, and industrial processes. These processes not only run with high reliability but also with high precision.
PLCs are designed to interact directly with real equipment. This means learning PLC programming requires more than just writing code. It involves understanding electrical systems, control logic, and industrial practices.
Beginners often feel overwhelmed by hardware concepts and vendor-specific software environments. This article explains how PLC programming can be learned step by step.
It starts from fundamental principles and gradually progresses. It moves toward practical, real-world applications used in industry today.
What is a PLC, and what does it do?
Before proceeding to the learning process, first, we should ask what a PLC actually does. A PLC is an industrial computer designed to monitor input signals. It executes a control program and updates output signals continuously.
This process happens in a repetitive loop known as the PLC scan cycle. During each scan, the controller reads the status of sensors and switches. It processes the logic written by the programmer.
It then sends a command to the outputs. This command is used to energize or de-energize actuators such as motors, valves, or indicator lamps. A clear understanding of the PLC’s internal structure is essential at this stage.
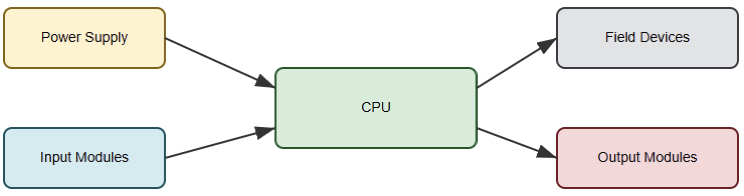
The PLC consists of a power supply and a central processing unit (CPU). It also includes input modules, output modules, and communication interfaces. Visualizing how these components interact helps beginners.
It helps them connect abstract logic to physical equipment. The next figure illustrates a basic PLC block diagram. It shows CPU, power supply, input modules, output modules, and field devices.
Learning Electrical and Control Fundamentals
PLC programming is closely tied to electrical control systems, and ignoring this foundation leads to confusion later.
Before writing programs, learners should understand how basic electrical components behave.
Traditional relay-based control systems are particularly important. PLC ladder logic was designed to replicate relay wiring diagrams.
This replication occurs in software form. When you understand how push buttons, contacts, relays, and contactors work, ladder logic becomes intuitive.
Instead of memorizing symbols, you begin to recognize familiar electrical behavior. That behavior is expressed digitally.
This foundation also improves troubleshooting skills. Many industrial problems are electrical rather than purely software-related.
The following figure indicates a side-by-side comparison. It shows the relationship of a relay control circuit and its equivalent ladder logic diagram.
Understanding Ladder Logic Programming
For any beginner, it is recommended to start with Ladder Logic (LD). This is because LD is the most common and beginner-friendly PLC programming language.
Its graphical format resembles an electrical ladder. Rungs represent control logic that flows from left to right. Inputs are shown as contacts, while outputs are represented by coils.
This visual structure allows programmers to quickly understand system behavior. This remains true even when viewing a program for the first time.
Beginners should start with simple control tasks such as a motor start-and-stop circuit. These examples introduce essential concepts like latching, interlocks, and safety stops. As confidence grows, timers and counters can be added.
They create delays, sequences, and repeated actions. At this point, clarity matters more than adding complexity.
It involves understanding why an output turns on. It also involves knowing what conditions turn it off.
The figure below depicts a simple motor start–stop ladder logic diagram with seal-in contact.
Understanding PLC Programming Standards
One of the requirements as a learner is to get familiar with international standards. IEC 61131-3 is one among these standards.
The latter is in charge of defining several programming languages. These languages are used across different PLC brands.
While ladder logic remains dominant, other languages are widely used in advanced applications.
These include Function Block Diagram and Structured Text. Structured Text resembles high-level programming languages.
It is useful for mathematical operations, data handling, and complex algorithms. Understanding these languages conceptually allows programmers to move between platforms more easily. It also helps them write more efficient control programs.
The upcoming figure specifies an overview diagram showing IEC 61131-3 programming languages. It also explains their typical applications
Choosing One PLC Platform
If you are a beginner, do not commit this common mistake. Learning multiple PLC brands at the same time.
Each manufacturer uses different software tools, memory structures, and workflows. This can slow down learning. It can also cause unnecessary confusion.
It is far more effective to choose one PLC platform and focus on mastering it. Learning how to configure hardware builds confidence. Assigning input and output addresses is also important.
Downloading programs and monitoring logic online builds strong foundational skills. A learner should focus on comprehending these concepts on one platform. After that, transitioning to another becomes much easier.
Practicing with PLC Simulators
Most of the modern software includes simulation tools. These tools allow programs to be tested without physical hardware.
Beginners should not take these tools for granted. This is because they are extremely valuable. In addition, they create a safe territory to experiment and make mistakes.
By toggling virtual inputs and observing outputs, learners can see behavior clearly. They can observe how their logic behaves in real time. Simulation also helps develop debugging skills.
Watching rungs energize and de-energize teaches how logic flows through a program. Over time, this builds the ability to predict system behavior. This occurs before downloading code to an actual controller.
Understanding the Main Parts of a PLC
A major milestone in learning PLC programming is understanding how the controller stores and processes data.
Inputs and outputs are mapped to memory addresses. Internal memory locations are used to store intermediate logic states, timers, counters, and data values.
One of the essential requirements to write cleaner and scalable programs is to learn how memory works.
It also makes troubleshooting much easier. The programmer can track how data moves through the control logic.
Understanding the difference between physical inputs and internal memory bits is especially important. This is critical when designing larger systems.
Learning from Real Industrial Applications
Theory alone is not enough to master PLC programming. Real learning happens when concepts are applied to practical systems.
Common industrial examples include motor control circuits with safety interlocks. Pump control systems are also common.
They often include automatic and manual modes. Basic process control applications are widely used.
Analyzing these systems teaches how to break a process into inputs, outputs, control logic, and safety conditions.
This system-oriented thinking is essential for professional automation work. Because it helps programmers design reliable and maintainable solutions.
Developing Troubleshooting Skills
Just like in any other engineering area, troubleshooting is an essential skill for any PLC programmer.
System downtime is a huge challenge in any industrial environment. To avoid this, systems must be repaired quickly.
Learning how to monitor logic online is essential. Checking input statuses is equally important.
Pinpointing blocking conditions is as vital as drafting new code. Mastering troubleshooting requires a significant dedication.
It also needs a blend of logical deduction and systematic testing. Experienced developers must differentiate between hardware failures and wiring flaws.
They must also identify software logic errors. This ability greatly increases confidence and professional value.
Gaining Hands-On Experience with Hardware
As it was mentioned above, learners should be familiarized with simulators. But simulation is powerful; dealing with real hardware is necessary. It provides insights that software alone cannot offer.
Physical systems introduce real-world factors such as wiring errors, signal noise, and sensor limitations.
Starting a very simple task is important. This could be a small training setup with push buttons as inputs.
In addition, indicator lights can significantly improve understanding. Hands-on practice reinforces safety awareness.
Plus, it teaches proper wiring techniques. It also helps learners appreciate how PLCs interact with actual industrial equipment.
Writing Clean and Documented Programs
In industry, PLC programs are rarely written for a single person. They must be readable by technicians, engineers, and maintenance staff.
Clear tag names and structured logic make programs easier to understand and maintain. Also, comments must be added.
Troubleshooting time can be reduced by good documentation. Also, it prevents costly mistakes.
Developing these habits early leads to more professional and reliable automation projects.
Conclusion
This article addressed the process of learning PLC programming by guiding readers from fundamental concepts to practical industrial applications.
As we all know, learning anything is a gradual journey. For this reason, learning PLC is not an exception. It combines theoretical understanding with hands-on experience.
By first grasping how PLCs operate, beginners build a strong foundation. Mastering ladder logic follows naturally. Applying knowledge to real-world systems completes the learning process.
Simulation tools and structured practice contribute to a deeper understanding. Without forgetting the troubleshooting experience.
So, learners should put effort into a clear and well-documented logic. In this way, PLC programming becomes an accessible and valuable skill. It opens opportunities in modern industrial automation.
FAQ: How to Learn PLC Programming
What is PLC programming?
It is writing control logic for industrial machines and processes.
Do I need electrical knowledge to learn PLCs?
Basic electrical concepts are helpful but not mandatory.
Which PLC language should beginners learn first?
Ladder Logic is the best starting point.
Do I need a real PLC to practice?
No. Simulators are enough at the beginning.
How long does it take to learn PLC programming?
Basics take a few months with regular practice.
Which PLC brand should I start with?
Start with one popular brand used in your region.
Are PLC skills still in demand?
Yes. PLCs are widely used in industry.
Can I learn PLC programming on my own?
Yes. Many engineers are self-taught.
What is the best way to practice PLCs?
Work on small, practical control examples.
Is PLC programming hard to learn?
It is manageable with step-by-step learning.