Industrial automation and process control form the foundation of modern industry. The factories use less human effort to run machines. Equipment can be automatically operated thanks to control systems used in automation.
Process control focuses on keeping variables within safe limits. These variables include level, flow, pressure, and temperature. Together, they improve productivity and safety. They also reduce errors and operating costs.
Many industries depend on these technologies today. For instance, include water treatment, oil and gas, power generation, and manufacturing.
For technicians and engineers working in industry, it is essential to understand these concepts.
This article studies the fundamentals of industrial automation and process control, their components, operation principles, and their role in modern industry.
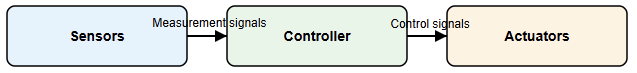
Definition of Industrial Automation
Industrial automation is the use of control systems to operate industrial processes. These systems reduce the need for manual operation. Because of the programmed logic, machines perform tasks automatically.
Automation improves consistency and speed. It also reduces human fatigue and mistakes.
Control devices monitor inputs and drive outputs. These devices work continuously without rest. Automation is used in simple machines and complex plants.
Definition of Process Control
Process control is a subset of industrial automation. It focuses on continuous processes. The goal is to maintain process variables at desired values. Controllers compare measured values with setpoints.
They then correct deviations automatically. Process control is common in chemical and thermal systems. It ensures product quality and system stability. Without control, processes can become unsafe.
Difference Between Automation and Process Control
Automation and process control are closely related. Automation covers a wide range of tasks.
These tasks include sequencing and logic operations. Process control focuses on continuous regulation.
Automation often uses discrete signals. Process control uses analog signals. Both work together in modern plants. A production line may use both methods at the same time.
Historical Background
Industrial automation began during the Industrial Revolution. Early systems relied on mechanical control.
Later, electrical relays were introduced. These relays enabled basic logic control. In the late twentieth century, PLCs became common.
Digital computers improved flexibility and reliability. Process control evolved with PID controllers. A larger number of these controllers are still widely used today.
Key Components
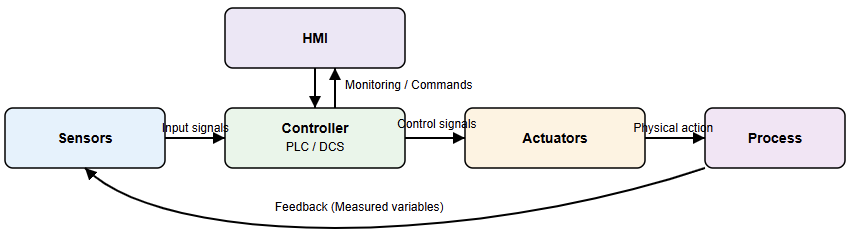
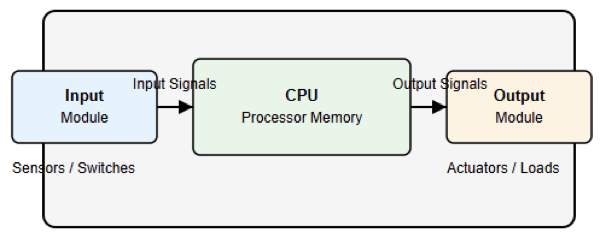
Industrial automation systems use several key components. The first ones are sensors which used to measure physical variables. Controllers process input signals. Actuators perform physical actions.
Power supplies energize the system. Communication networks link all devices. Each component has a specific role. Together, they form a complete control system.
Sensors and Instrumentation
Sensors detect changes in physical conditions. They convert these changes into electrical signals. Common sensors measure temperature and pressure. Others measure flow and level.
Accurate sensing is critical for control. Poor sensors cause poor control performance. Instruments must be calibrated regularly. Reliability is very important in industrial environments.
Controllers in Automation Systems
Controllers are the brain of automation systems. They receive signals from sensors. They execute control logic or algorithms. PLCs are widely used controllers. DCS systems handle large continuous processes.
Controllers make decisions in real time. They send commands to actuators. Their speed and reliability are crucial.
Actuators and Final Control Elements
Actuators carry out control actions. They convert control signals into motion or force. Motors drive conveyors and pumps. Valves regulate fluid flow.
Actuators must respond quickly and accurately. Poor actuator performance affects the whole process. Selection depends on load and environment.
Control Strategies in Process Control
Different strategies are used in process control. On-off control is the simplest method. PID control is the most common method.
It combines proportional, integral, and derivative actions. Advanced strategies include cascade control. Model predictive control is also used. The choice depends on process dynamics.
Feedback Control Systems
Feedback control is widely used in industry. The system measures the output continuously.
The controller compares it to the setpoint. Any error is corrected automatically. This method improves stability and accuracy. Feedback systems handle disturbances well. They are simple and reliable.
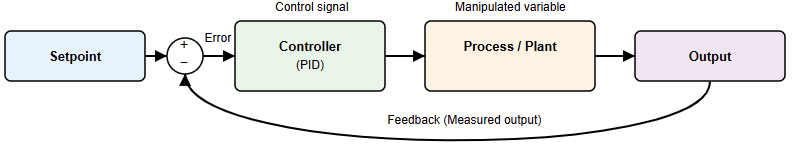
Open-Loop Control Systems
Open-loop control does not use feedback. The controller sends commands without checking results.
These systems are simple and low-cost. They are used when accuracy is not critical. Disturbances are not corrected automatically. Open-loop control is less flexible.
Industrial Communication Networks
Devices must exchange data reliably. For this reason, communication is vital in automation systems. Common protocols include Modbus and Profibus. Ethernet-based networks are increasingly popular.
Industrial networks are robust and deterministic. They support real-time control. Good communication improves system integration.
Human-Machine Interface
It is famously known as HMI. The HMI connects operators to machines. It displays process data clearly. Operators can start or stop equipment.
Alarms warn of abnormal conditions. HMIs improve usability and safety. They reduce operator errors. Modern HMIs use graphical touch screens.
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition System
It is also known as the SCADA system. The SCADA systems monitor large processes. They collect data from remote sites.
Operators supervise operations centrally. SCADA is common in utilities and pipelines. It supports data logging and alarms. Remote control improves efficiency. Cybersecurity is very important in SCADA systems.
Safety in Industrial Automation
Automation systems must meet strict safety requirements. Systems must prevent hazardous conditions.
Safety PLCs are often used. Interlocks protect personnel and equipment. Emergency stop circuits are mandatory. Standards guide safe system design. Proper testing is essential.
Impacts of Industrial Automation
Automation offers many benefits to the industry. It increases production efficiency. Product quality becomes more consistent.
Operating costs are reduced over time. Safety is significantly improved. Downtime is minimized with monitoring. Data helps optimize processes.
Challenges and Limitations
Challenges are everywhere in technology systems; automation is not an exception. Initial costs can be high. Skilled personnel are required.
System complexity can increase. Cybersecurity risks must be managed. Maintenance is still necessary. Proper planning reduces these issues.
Applications Across Industries
Industrial automation is used in many sectors. Manufacturing uses robots and PLCs. Oil and gas use process control systems.
Power plants rely on automation heavily. Water treatment uses automated control. Food processing depends on precise control. Each industry has unique requirements.
Future Trends in Automation
The existence of Industry 4.0 is a key proof that automation continues to evolve rapidly. IoT enables remote monitoring. Artificial intelligence improves decision-making.
Digital twins simulate processes. Systems become more connected and intelligent. Engineers must keep learning.
Conclusion
This article reviewed the core concepts of industrial automation and process control. Industrial automation and process control are essential technologies. Industrial automation and process control are essential technologies.
They enable safe and efficient industrial operation. Automation handles logic and sequencing tasks.
Process control maintains stable operating conditions. Together, they improve productivity and quality. Modern industries rely on these systems daily.
Understanding their principles is very important. Technicians and engineers benefit from strong knowledge in this field.
Every day, there is an advancement in technology. For this reason, automation will continue to grow in importance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is industrial automation?
It is the use of control systems to operate machines and processes automatically.
What is process control?
It regulates process variables to keep operations stable and safe.
How are automation and process control related?
Automation handles logic and sequences, while process control manages continuous variables.
What are common process variables?
Temperature, pressure, flow, and level.
What devices are used in automation systems?
Sensors, controllers, actuators, and communication networks.
What is a PLC?
A PLC is an industrial computer used to control machines and processes.
Where are these systems used?
In manufacturing, power plants, oil and gas, water treatment, and food processing.
Why is process control important?
It improves safety, efficiency, and product quality.
Can automation be added to existing systems?
Yes, most systems can be upgraded or integrated.
Do these systems use HMIs or SCADA?
Yes, they provide monitoring, control, and alarms.
