A capacitive proximity sensor is a contactless sensing device. It is designed to detect the presence of nearby objects. It functions based on the principle of capacitance. Inductive sensors detect only metal.
Capacitive sensors detect both conductive and non-conductive materials. This makes them useful in industrial automation. They are used for level measurement. They are also used for counting and position monitoring.
This article explains the fundamentals of capacitive proximity sensors. It presents their structure and working principle. It also describes their applications and benefits. Understanding how they work is important for automation and control engineers.
A Capacitive Proximity Sensor
A capacitive proximity sensor is a contactless sensing device. It is designed to detect the presence of nearby objects. It functions based on the principle of capacitance. Inductive sensors detect only metal.
Capacitive sensors detect both conductive and non-conductive materials. This makes them useful in industrial automation. They are used for level measurement. They are also used for counting and position monitoring.
This article explains the fundamentals of capacitive proximity sensors. It presents their structure and working principle. It also describes their applications and benefits. Understanding how they work is important for automation and control engineers.
The Principle of Operation
The working mechanism is based on the concept of a capacitor. A capacitor stores energy within an electric field. In a capacitive sensor, the sensing face acts as one plate of a virtual capacitor. The target object serves as the second plate.
The air or other material between them forms the dielectric. The sensor continuously monitors the capacitance between its internal plate and the surrounding environment.
Key Components
A capacitive proximity sensor consists of several internal sections. These parts work together to detect objects effectively.
The Sensing Electrode (Plate)
This is the active part of the sensor. It is usually a flat metal disc at the sensor’s front. It emits the electric field. Its geometry and dimensions define the detection distance and field pattern.
The Oscillator
The oscillator produces a high-frequency alternating voltage. It typically operates in the megahertz range. This voltage is applied to the electrode to create the electrostatic field.
The Trigger Circuit
This circuit observes the oscillator’s amplitude. When a target nears the sensor, capacitance rises. This causes a change in amplitude. The trigger circuit compares this signal to a threshold. It switches the output on or off accordingly.
The Output Stage
The output section transmits the electrical signal to external devices. It may use a transistor (NPN/PNP), a relay, or a voltage output. This stage interfaces with PLCs, counters, or alarms.
The next figure indicates cross-section diagram of a capacitive proximity sensor showing the oscillator, electrode plate, trigger circuit, and output stage.
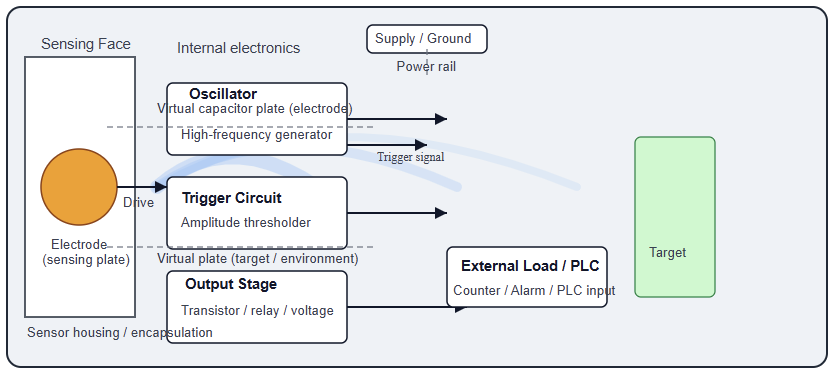
How It Works: Step-by-Step
The detection process involves a sequence of electrical reactions:
- The oscillator generates an electric field at the sensing face.
- This field extends into the surrounding space.
- When a target approaches, it enters the field region.
- The object alters the dielectric characteristics of the medium.
- This change increases the capacitance of the sensor’s virtual capacitor.
- The oscillator’s amplitude is affected by the capacitance variation.
- The trigger circuit detects this alteration.
- The output stage activates and sends a detection signal.
- When the object departs, capacitance returns to normal.
- The output resets to its original state.
Detecting Different Materials
Capacitive sensors can detect a wide range of substances. Detection depends on each material’s dielectric constant (ϵr). The dielectric constant shows how well a material stores electrical energy.
Air has a dielectric constant near 1. Water has a value of about 80. Metals have extremely high constants. Materials with higher dielectric constants are easier to sense.
- Water, liquids, and moist: Substances with high ϵr are easily detected.
- Plastics, paper, and wood: Possess medium ϵr can be detected at shorter distances.
- Air: Contains low ϵr reserves as the reference baseline.
The figure below shows a bar chart comparing dielectric constants for air, water, oil, plastic, wood, and metal.
Key Features and Adjustments
Capacitive sensors have some adjustable features, which are detailed in this section.
Sensing Range
The sensing distance is the farthest point at which an object can be detected. It usually ranges from a few millimeters to several centimeters. The range depends on sensor size and the target material.
Sensitivity Adjustment (Trimmer)
Most sensors include a sensitivity control, often a small potentiometer. It allows fine-tuning of the detection threshold. This adjustment helps eliminate background interference. It can also focus the detection on specific materials.
Shielding
The sensor’s sides and rear are usually shielded. This prevents interference from nearby structures. It also concentrates the electric field forward for accurate detection.
Applications of Capacitive Sensors
Capacitive proximity sensors are widely used in industrial automation. Their robustness and versatility make them ideal for many uses.
Level Sensing
They are ideal for measuring liquid or solid levels inside non-metallic tanks or containers. They can even detect materials through the container wall. This feature makes them suitable for chemical and food processing environments.
Object Counting
On conveyor systems, they count items such as bottles, boxes, or other packaged goods. They can detect items regardless of the material type.
Position Detection
They verify the presence or alignment of machine components. This helps ensure that a part is in place before the next operation begins.
Moisture Detection
Changes in dielectric constant can reveal moisture levels in materials like paper, wood, or grain. This allows for indirect humidity measurement.
Advantages and Disadvantages
This section details the pros and cons of proximity sensors.
Advantages
Capacitive sensors are contactless. This minimizes mechanical wear. They can detect many types of materials. They also perform well in dusty or contaminated environments. In addition, they are cost-effective and durable.
Disadvantages
They are sensitive to environmental changes such as humidity and temperature. These variations may cause drift or false triggering.
Their sensing range is relatively short. They often require periodic recalibration. Their wider sensing field can also complicate installation in tight spaces.
Capacitive vs. Inductive Sensors
This section shows the comparison of capacitive and inductive sensors. By comparing the two helps clarify their best use cases.
- Inductive sensors detect only metallic targets using magnetic fields. They are less affected by dirt or moisture.
- Capacitive sensors detect both metals and non-metals, including liquids and powders. They use electric fields instead of magnetic ones. While more flexible, they require careful adjustment and setup.
The final choice depends on the sensing requirements of each application.
Installation Considerations
Proper mounting ensures consistent performance. The sensor should be securely fixed and oriented directly toward the target. Shielding helps minimize false triggers from nearby objects.
Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity should be considered. These conditions can influence sensor stability.
Detailed mounting guidelines and technical datasheets are available from major manufacturers. Examples include Omron and Sick AG.
Key takeaways: What is a Capacitive Proximity Sensor?
This article reviewed the fundamentals, operation, and applications of capacitive proximity sensors. A capacitive proximity sensor is a non-contact device. It detects materials by measuring changes in capacitance.
Its internal components work together to ensure accurate detection. These components include the oscillator, the sensing electrode, the trigger circuit, and the output stage.
These sensors are used for level sensing.
They are also used for object counting and position monitoring. They need proper installation. They also need periodic calibration. Despite this, they remain highly versatile and reliable.
They perform well in environments that require contactless detection. Capacitive sensors play an important role in modern industrial automation. They support efficient control and monitoring.
FAQ: What is a Capacitive Proximity Sensor?
What is a capacitive proximity sensor?
It is a non-contact sensor that detects objects by measuring changes in capacitance. It can sense both metallic and non-metallic materials.
How does it work?
It creates an electric field at the sensing face. When an object enters this field and changes the capacitance, the sensor switches its output.
What materials can it detect?
It can detect metals, plastics, wood, glass, liquids, powders, and most materials with a measurable dielectric constant.
How is it different from an inductive sensor?
Inductive sensors detect only metals using magnetic fields. Capacitive sensors detect many materials using electric fields.
What are common applications?
Level detection in tanks, object counting on conveyors, position sensing, and detecting moisture in materials.
What affects installation and performance?
Humidity, temperature, nearby objects, grounding, and sensor orientation. Sensitivity adjustment is often required.
What are the advantages?
Non-contact operation, ability to detect many materials, and reliable performance in dusty or dirty environments.
What are the disadvantages?
Shorter sensing range and sensitivity to environmental changes like humidity and temperature.
Why do false triggers occur?
Changes in humidity, temperature, or nearby conductive objects affecting the electric field. Adjusting sensitivity or shielding helps.
Can it detect through non-metallic walls?
Yes. It can detect liquids or solids through plastic or glass containers because the electric field penetrates non-metallic materials.