Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are specialized computers used in industrial automation.
In order for PLCs to run must have some instructions or programming languages inside their CPU.
The most famous languages like Ladder Logic (LD), Function Block Diagram (FBD), and Structured Text (ST) are under standard of International Electrotechnical Commission IEC-61131-3.
This organization is in charge of defining standard of several programming languages for PLCs
In this article we are going to see the foundation of each one, their advantages and disadvantages, and finally we will conclude by how to choose one.
Ladder Logic (LD)
Ladder Logic is a graphical programming language that is the oldest and most widespread of the IEC 61131-3 standards. It was designed to resemble the electrical diagrams of relay-based control systems.
Structure of Ladder Logic
The structure of Ladder Logic has two vertical bars representing the power line connected by horizontal “rungs” that contain the logic as shown in the figure below.
From the figure, the rungs are read from left to right and top to bottom. This simulates the physical flow of power through contacts (X) and coils (Y) to control output devices.
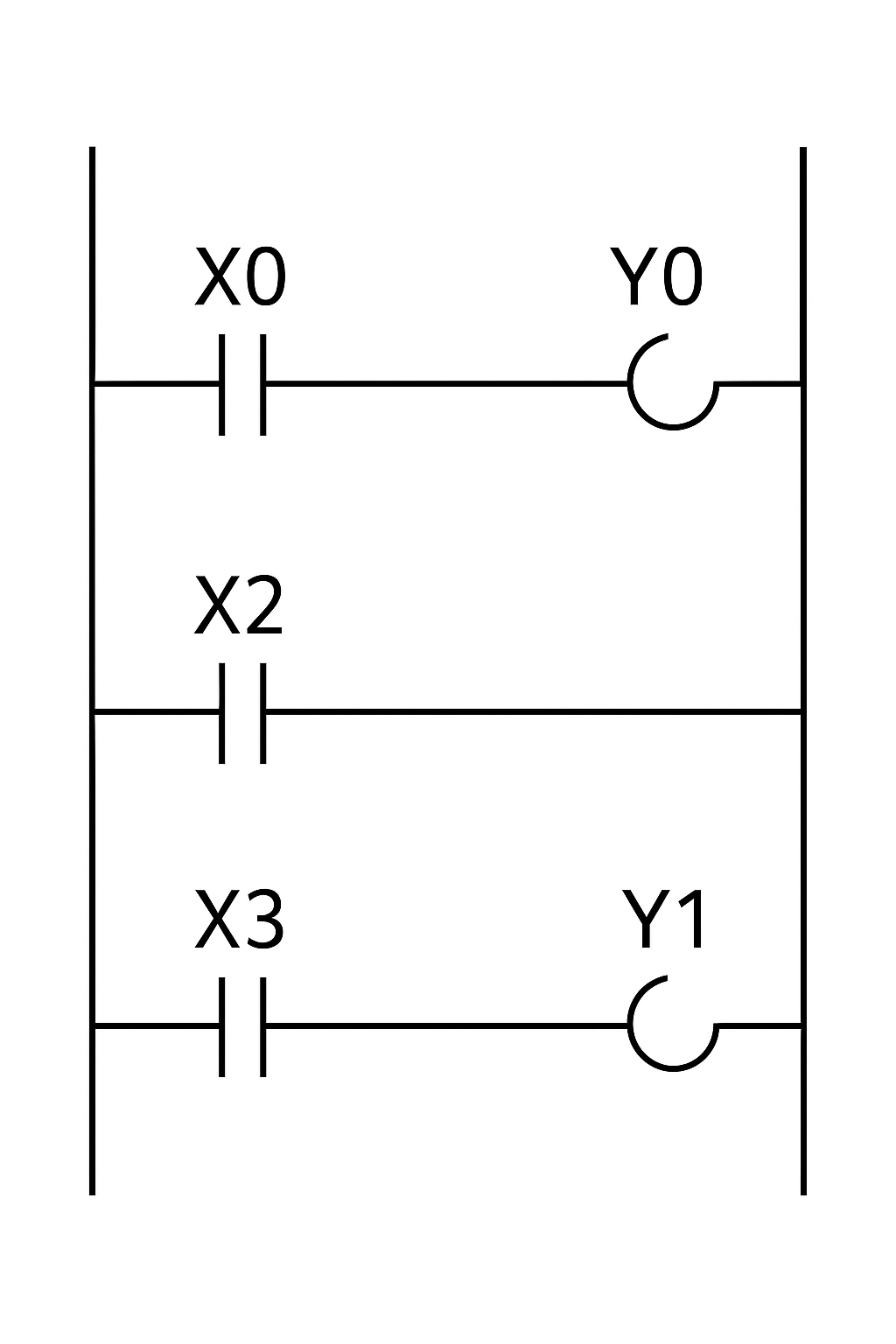
Structure of Ladder Logic
Advantages of Ladder Logic
Simple for beginners
For fresh engineers, technicians and electricians, Ladder Logic is highly comfortable.
Easy Debugging
Modern PLC software can animate Ladder Logic diagrams, highlighting active elements as the program runs. This provides real-time feedback, allowing you to quickly trace the logic flow.
Ideal for Discrete Logic
Ladder Diagram is highly effective for straightforward on/off control.
Broad Familiarity
With its long-standing use in industry, Ladder Diagram is the most widely adopted PLC language.
Disadvantages of Ladder Logic
Data Handling Limitations
Ladder Logic is not naturally designed for working with complex data types such as arrays or strings.
Low Portability
Compared to Structured Text, Ladder Logic is harder to transfer between different PLC platforms.
Differences in vendor-specific instructions and graphical layouts often mean programs must be rewritten from scratch.
Complexity Management Issues
Ladder Logic diagrams can become crowded with numerous rungs and intricate interconnections.
This visual complexity makes large programs difficult to read, troubleshoot, and maintain.
Weakness in Calculations
LD is inefficient for advanced arithmetic, algorithms, or heavy data manipulation. Implementing such tasks typically produces bulky code that is harder to understand and less efficient than text-based approaches.
Function Block Diagram (FDB)
Function Block Diagram is a graphical language that represents the program as a network of interconnected blocks.
Inside the block there may be other languages embedded such as Ladder Logic or any of the other PLC languages.
Structure of Function Block Diagram
The figure below illustrates the structure of the Function Block Diagram. Notice that the block named function could be performing any specific task, such as a timer, a counter, PWM block, a PID controller, or a custom-defined function.
Data and signals flow from the output of one block to the input of another, creating a clear visual representation of the program data flow.
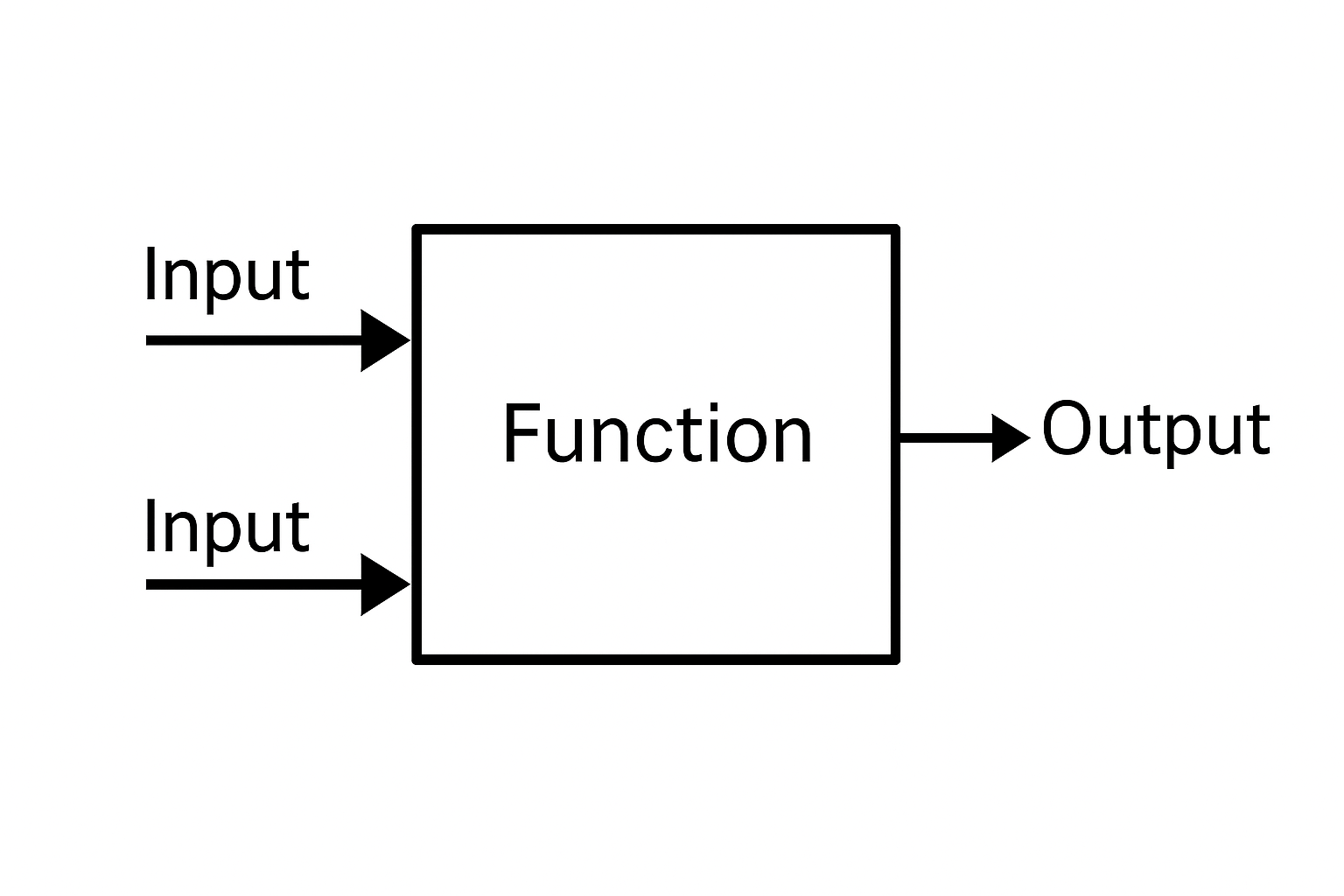
Structure of Function Block Diagram
Advantages of Function Block Diagram
Reusable Modular Design
One of Function Block Diagram main advantages is its modular structure. Developers can build custom function blocks for specific tasks and reuse them across different programs or projects.
Clear Troubleshooting
FBD environments often provide animated data flow, making it easy to trace signals as they move between blocks.
This visual feedback helps technicians quickly identify where a value is being created, modified, or interrupted.
Language Flexibility
Many PLC platforms allow Function Block Diagrams to work seamlessly with other programming languages.
For example, an FBD routine can be called from Ladder Logic, enabling developers to apply the most appropriate language for each task within a project.
Process Control Strengths
FBD is particularly effective for continuous control applications, such as tuning PID loops for variables like temperature, flow, or pressure.
The graphical, block-based structure makes it easy to visualize how data moves and changes through the system.
Clear Representation of Complex Systems
Unlike Ladder Logic, which can become difficult to follow in large programs, FBD organizes operations into compact, functional blocks.
This provides a cleaner, more understandable view of complex logic, simplifying both analysis and maintenance.
Disadvantages of Function Block Diagram
Harder to learn
While more intuitive than Structured Text, FBD can be more challenging for beginners and maintenance staff to grasp compared to the straightforward relay logic of Ladder Logic.
Potentially complex layout
For very large and complex systems, the diagram can still become a maze of interconnecting lines and blocks.
While still generally cleaner than complex LD, poor organization can hinder readability.
Overhead for simple tasks
For basic discrete logic, FBD can feel like overkill. Simple on/off logic is often faster and easier to implement directly in Ladder Logic.
Structured Text (ST)
Structured Text is a high-level, text-based programming language that uses a syntax similar to Pascal or C.
It is the most powerful and flexible of the IEC-61131-3 languages. So, offers advanced features like loops, conditional statements, and complex data structures.
Structured Text is ideal for programmers with a traditional software background, as it closely mirrors the programming languages, they are familiar with.
Structure of ST
The following figures shows the structure of ST language. Notice the resemblance with the other high level programming languages like Pascal and/or C.
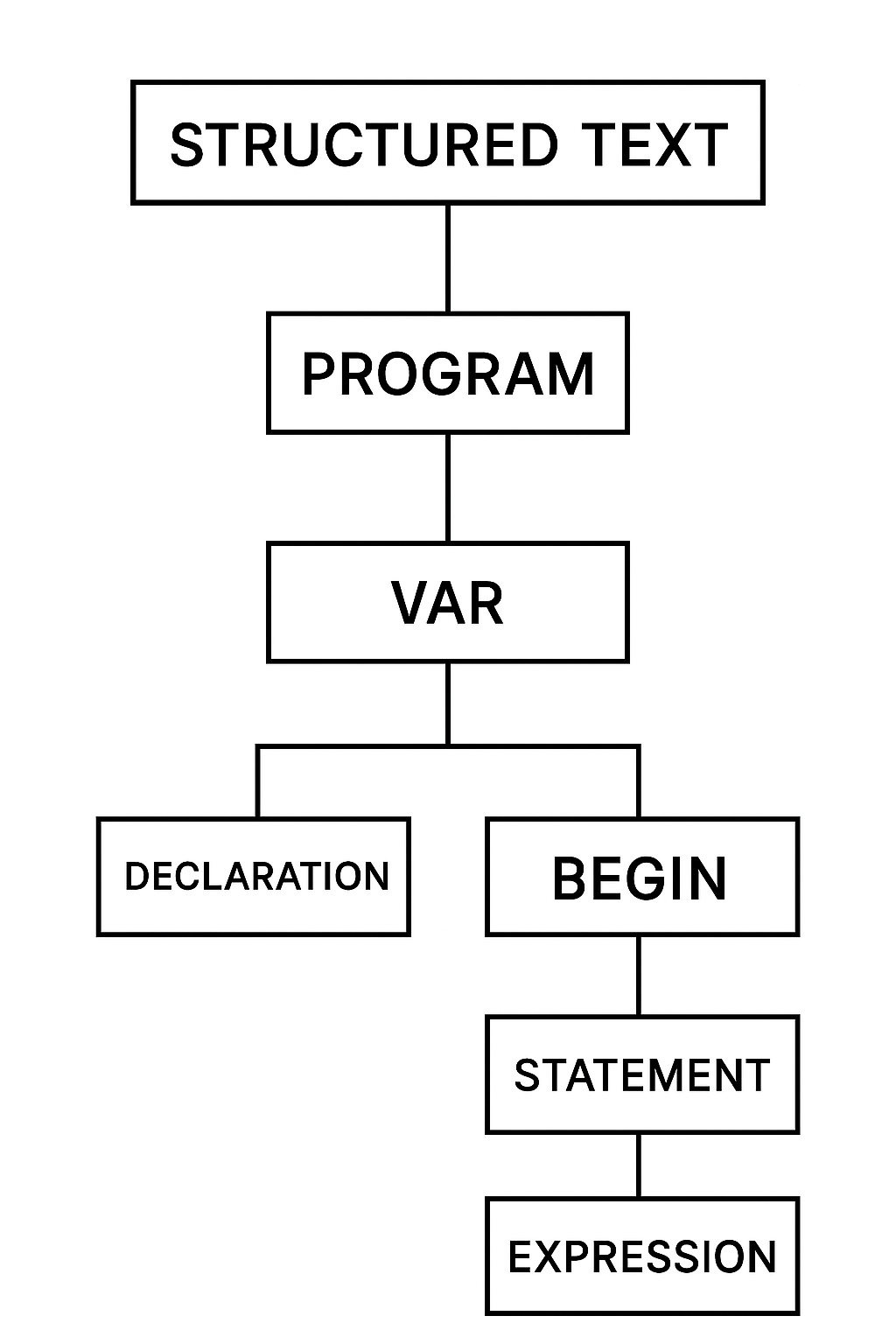
Structure of ST language
Advantages of Structured Text
Efficiency for complex tasks
ST is excellent at handling complex mathematical calculations, data manipulation, and advanced algorithms. It can perform these tasks in a compact, efficient manner.
Modularity and portability
ST code is highly modular, supporting functions and function blocks that can be easily reused.
Because it is text-based, it is also the most portable language between different PLC manufacturers that adhere to the IEC standard.
Compact code
The text-based format of ST makes the code much more compact than the graphical representations of LD and FBD. This can reduce the program size and memory usage.
Advanced control structures
ST provides advanced programming constructs like FOR, WHILE and REPEAT loops, as well as CASE statements, which are very difficult or impossible to implement cleanly in Ladder Logic.
Data handling
ST is a natural fit for working with strings, arrays, and complex data types, making it ideal for tasks like data logging, report generation, and communication protocols.
Disadvantages of Structured Text
Hard to Learn
The biggest drawback of ST is its lack of visual representation, making it less intuitive for maintenance technicians without a programming background.
Troubleshooting a problem requires a deeper understanding of the code rather than simply looking at a visual flow.
Debugging challenges
While modern IDEs offer watch windows to monitor variable states, debugging ST is generally more abstract than the visual animation provided by graphical languages.
Higher entry barrier
ST requires a higher level of programming knowledge to use effectively, which can increase training costs and limit the pool of available personnel.
Poor readability for simple logic
While excellent for complex tasks, Structured Text can be less readable and less immediately clear than Ladder Logic for simple, discrete logic sequences.
A straightforward interlocking circuit is much more intuitive when represented graphically.
What Language to Use?
The choice between Ladder Logic, Function Block Diagram, and Structured Text is not a matter of one being inherently superior, but rather of selecting the right tool for the specific application and environment.
For simple, discrete logic and high-speed troubleshooting
Ladder Logic is the clear winner. Its visual nature aligns with the skills of electrical and maintenance personnel, minimizing downtime when problems arise.
For complex, continuous processes and modularity
Function Block Diagram is the better choice. It provides a clean, modular structure for complex algorithms like PID control and makes data flow easy to follow.
For complex math, data handling, and large projects
Structured Text is the most powerful and efficient. It offers the flexibility and advanced control structures needed for sophisticated, algorithm-intensive applications.
In reality, most modern industrial projects use a combination of these languages within the same PLC program.
A common approach is to use Ladder Logic for simple I/O and discrete control, while using Function Blocks for analog control and Structured Text for complex calculations or data manipulation.
This blended strategy leverages the strengths of each language, creating a robust, efficient, and maintainable program that is accessible to a wider range of technical personnel.
Conclusion
This article reviewed three PLC programming languages, Ladder Logic, Function Block Diagram, and Structured Text. It also studied the foundation of each one, their advantages and disadvantages.
Finally, it showed an analysis of which language to choose between the three. So, any language of the three can be chosen depending what function, projects, or what is you are trying to achieve in your application.
FAQ: Ladder Logic vs Function Block diagram vs Structured Text
What are these languages—and are they officially recognized?
Ladder logic (LD), Function Block Diagram (FBD) and Structured Text (ST) are standard PLC programming languages. Yes, they are recognized under IEC-61131-3 standard.
What is the origin and core purpose of each?
The LD was designed to get rid of relay-control systems due to larger numbers of relay in one system. FBD for reusable modular and ST to get high level languages advantage.
What are the strengths of each?
LD is simple good for those who start to learn about PLC. FBD is modular, so good for large scale project. While ST is better for complex data manipulation
What are the challenges or limitations of each language?
LD is not well for data manipulation, FBD may have complex layout when it comes to big program and ST as it’s high-level language, hard to learn and debug.
Which language is best for which scenarios?
LD simple to learn and for simple calculation, FBD for its modularity and ST for data manipulation and complex projects.
Is it common to use multiple languages in one project?
Yes, for example a PID controller block in many PLC as been implemented using all these languages.
Which language should beginners learn first?
Ladder Logic is usually the best starting point due to its intuitive visual nature and strong prevalence across PLC systems. Once you are comfortable, you can expand into FBD the ST.