The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a vast network of connected physical devices. These devices communicate and share information over the internet. Automation, on the other hand, uses technology to perform tasks without direct human input.
When these two concepts combine, they create powerful, intelligent ecosystems capable of learning, adapting, and optimizing themselves over time.
IoT devices gather large amounts of data from the physical environment, while automation systems process this data to make smart decisions.
This continuous exchange between sensing and action forms the foundation of modern intelligent systems.
Their integration is transforming industries such as manufacturing, logistics, agriculture, energy, and even home systems.
The result is improved efficiency, productivity, and convenience in nearly every field. Businesses can make better, faster decisions, while consumers enjoy more personalized and energy-efficient experiences.
This article explores how IoT and automation complement each other and function together as a unified system driving modern technological progress.
It also highlights the underlying architecture, challenges, and future trends shaping this powerful alliance.
Data Collection with IoT
At its core, IoT focuses on data gathering. It involves physical devices equipped with sensors, microcontrollers, and connectivity features. These devices can measure, monitor, and transmit data from their surroundings in real time.
Common examples include temperature sensors in HVAC systems, vibration sensors on motors, GPS trackers in vehicles, and smart meters in power grids.
The data collected can include variables such as temperature, pressure, vibration, speed, energy usage, humidity, or even chemical composition.
This data provides insight into the performance and condition of machines, environments, and systems. Once gathered, the data is transmitted to a centralized platform or the cloud for further analysis.
Wireless technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, LoRaWAN, and cellular networks enable this transmission, depending on the range and data requirements.
The sheer scale and diversity of the data provide the foundation upon which automation operates.
Without IoT’s ability to collect up-to-date and accurate data, automation systems would lack the real-time intelligence required to make informed decisions.IoT also plays a key role in predictive and preventive maintenance.
For instance, sensors can detect early signs of wear in rotating machinery, allowing automated systems to schedule maintenance before a failure occurs. This ability to monitor continuously and act preemptively is one of IoT’s greatest strengths.
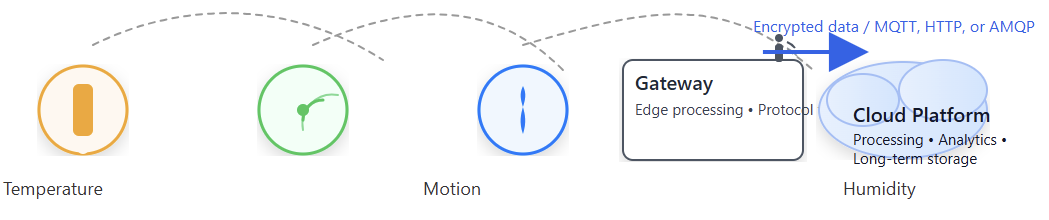
The following figure illustrates a diagram depicting how IoT sensors, such as temperature, motion, and humidity sensors, send data wirelessly to a gateway, which forwards it to a cloud platform for processing.
This figure illustrates the movement of data from the physical world into the digital domain, where automation can take over.
The Role of Automation
Automation executes specific actions based on programmed logic or rules. It is what transforms data into real-world responses.
Historically, automation was limited to simple, rule-based triggers, such as turning on a motor when a button was pressed.
Today, with IoT integration, automation becomes far more dynamic and data-driven. It processes incoming IoT data in real time to make decisions and perform tasks. For instance, a manufacturing line might automatically slow down if sensors detect overheating.
This prevents potential damage and ensures safe operation. Likewise, a building automation system might close blinds when light levels are too high. These responses improve safety, comfort, and efficiency simultaneously.
Automation provides the “response” or “action” aspect of IoT’s “sensing” ability, creating a continuous feedback loop between data and execution.
This loop enables systems to adapt to changing conditions without waiting for human intervention.
Furthermore, modern automation often uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to refine its decision-making processes.
Over time, systems can learn patterns, such as daily energy consumption trends or machine performance baselines, and optimize themselves for better outcomes.
The Integration Architecture
This collaboration between IoT and automation occurs through multiple stages. First, IoT sensors collect data from the environment.
Next, the data is transmitted to a processing unit, either locally (edge computing) or remotely (cloud computing).
The information is then analyzed and compared against predefined rules, thresholds, or AI-driven models. Finally, an automated response is triggered in the form of a physical or digital action.
This entire sequence can happen within milliseconds, depending on the application.
For example, in a robotic assembly line, sensors detect object positions, processors analyze the data, and actuators adjust their movement all in real time.
Edge computing enables data processing close to where it is generated, which reduces latency and enhances reliability. This is particularly important in time-sensitive applications like autonomous vehicles or industrial safety systems.
Meanwhile, cloud computing supports large-scale analytics, historical data storage, and remote system management.
Together, they form a hybrid architecture that ensures seamless data collection, analysis, and action, allowing distributed systems to function as a unified intelligence network.
The next figure indicates a diagram showing sensors transmitting data to edge devices, which forward selected data to the cloud.
The cloud analytics system then sends commands to actuators like valves and motors. This figure shows the main components and data flow in a connected IoT-automation system.
Smart Homes as an Example
Smart homes clearly demonstrate the practical benefits of integrating IoT and automation. An IoT motion sensor might detect movement in a room and send the data to a central hub.
The automation logic could then specify, “If movement is detected after 6 PM, turn on the lights.” The system would automatically activate the smart switch, improving comfort and energy efficiency.
Similarly, smart thermostats use temperature and humidity sensors to adjust heating or cooling based on user preferences and outdoor conditions.
Voice assistants like Alexa or Google Home use IoT connectivity to integrate various devices.
These include lighting, security cameras, appliances, and entertainment systems. Together, they form one seamless automation network.
These systems not only improve convenience but also reduce energy consumption and increase security.
For instance, smart locks can automatically secure doors when sensors detect no movement in the house. Leak sensors can also send instant alerts to the homeowner. They can even trigger water shutoff valves to prevent damage.
Smart homes illustrate the essence of IoT and automation: constant awareness through sensors and immediate, intelligent action through automation.
Industrial Automation and the IIoT
In the industrial sector, this integration is referred to as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). It combines traditional industrial control systems with modern IoT connectivity and advanced analytics.
Sensors installed on machines monitor conditions such as vibration, temperature, current draw, and lubrication levels. These sensors provide valuable data that reflects the machine’s operating state.
Automation systems then use these readings to detect abnormalities and predict maintenance needs.
For instance, if a motor’s vibration pattern changes significantly, the system automatically schedules maintenance before a breakdown occurs.
This proactive approach helps prevent costly downtime and improves equipment reliability. IIoT also enhances production efficiency. Automation can adjust conveyor speeds and optimize resource use.
It can also balance production loads based on real-time data from sensors. When integrated with enterprise systems like ERP or MES, IIoT ensures that production aligns with material availability. It also keeps operations in sync with demand forecasts.
The result is a smarter, safer, and more sustainable manufacturing environment. Additionally, IIoT supports remote monitoring and control. Engineers can access live machine data from anywhere in the world using secure digital platforms.
The upcoming figure depicts a diagram showing factory machines with sensors sending data to a monitoring system.
This system can trigger automated maintenance or adjust production speeds. The figure demonstrates how IIoT enhances manufacturing operations through data-driven automation.
Data Analytics for Smarter Automation
The vast quantities of data collected through IoT are valuable only when analyzed effectively. Data analytics converts raw sensor data into meaningful and actionable insights.
It helps identify trends, detect anomalies, and support decision-making processes. Modern analytics tools use machine learning and artificial intelligence to continuously refine automation rules.
For example, an HVAC automation system might learn to anticipate occupancy patterns. It can then adjust temperature and airflow proactively to maintain comfort and save energy.
Similarly, predictive models can forecast equipment failures based on subtle variations in sensor readings. This allows maintenance teams to act before breakdowns occur. Analytics bridges the gap between sensing and action.
It gives automation the intelligence needed to evolve and improve over time. With the help of big data analytics, organizations can optimize operations ranging from supply chains to energy management. This leads to higher productivity and reduced waste.
As data continues to grow in both scale and complexity, AI-driven analytics will play an increasingly central role. It will be essential for achieving autonomous, self-correcting systems that can adapt without human input.
Challenges of Integration
While the benefits of IoT and automation are immense, their integration also presents significant challenges. Cybersecurity remains one of the most critical concerns in this field.
Billions of connected devices create countless potential entry points for cyberattacks. Protecting sensitive industrial and personal data is essential. It ensures both trust and safety across connected systems.
Interoperability poses another major challenge. Different manufacturers often use varying communication protocols and standards. This variation makes it difficult for devices to communicate seamlessly.
Establishing universal standards and promoting open-source platforms can help reduce this issue and improve compatibility.
Data management is equally complex. The massive volume of data generated by IoT devices demands high-capacity storage and fast processing systems.
It also requires efficient filtering to extract meaningful and relevant information. Organizations must invest in scalable cloud or edge infrastructure to handle this workload effectively and reliably.
Finally, implementing IoT-automation systems involves significant initial investment and skilled personnel.
Proper training, ongoing maintenance, and strong data governance are all crucial for dependable operation.
Addressing these challenges will ultimately determine how successfully industries can harness the full potential of IoT and automation.
The Future of IoT and Automation
The next stage in this evolution is the rise of fully autonomous systems. These systems can sense, analyze, and act completely without human intervention. They represent the highest level of integration between IoT and automation.
Self-driving cars are one of the most visible examples of this technology. They rely on a network of IoT sensors such as LiDAR, radar, and cameras. These sensors continuously feed large amounts of data to automation algorithms.
The algorithms process this data in just milliseconds to make real-time navigation decisions and ensure safe driving.
In logistics, smart warehouses use IoT to track inventory in real time. Automation then controls robotic arms and conveyors that move products efficiently through the facility.
Drones equipped with sensors can monitor crop health and automatically apply fertilizers where needed. This combination boosts productivity and reduces human labor.
Smart cities represent another major frontier for IoT and automation. Connected traffic systems can adjust light timings dynamically based on traffic flow. Waste management systems can use sensor data to optimize collection routes and reduce fuel consumption.
Even power grids are becoming “smart.” They balance supply and demand automatically through intelligent energy distribution systems.
The ultimate goal is a world where systems self-regulate and optimize performance in real time, making life safer, cleaner, and more efficient for everyone.
Conclusion
This article reviewed how IoT provides the sensing and data-gathering capability. Automation, on the other hand, delivers decision-making and action.
Together, they form intelligent systems that can sense, analyze, and respond to real-world conditions. These systems operate without the need for human involvement.
This powerful combination enhances operational efficiency and reduces errors. It also promotes continuous improvement across many industries.
In homes, it creates comfort and energy savings. In manufacturing, it improves productivity, safety, and reliability.
The integration also drives innovation in areas such as smart cities, logistics, and autonomous vehicles. As IoT devices become more advanced, automation systems also grow more capable.
With the help of artificial intelligence and machine learning, their synergy will lead to smarter, self-adapting environments.
The ongoing evolution of these technologies is transforming how machines work. It is also redefining how people interact with their surroundings.
This progress paves the way for a more connected, intelligent, and efficient world, one where data and automation work hand in hand to shape the future of technology and human life.
FAQ: IoT and Automation
What is IoT?
IoT is a network of physical devices that collect and share data using sensors and connectivity.
What is automation?
Automation uses technology to perform tasks or make decisions with little or no human help.
How do IoT and automation work together?
IoT gathers data from the environment, and automation uses that data to take real-time actions.
What are the benefits of combining them?
They improve efficiency, reduce errors, save energy, and enable smarter decision-making.
Where are they used?
In smart homes, factories, logistics, energy systems, and smart cities.
What is IIoT?
The Industrial Internet of Things applies IoT and automation to factories for better monitoring and control.
What challenges exist?
Key challenges include security risks, data overload, and device compatibility.
How does AI help?
AI analyzes IoT data to make automation smarter and more adaptive.
What is edge computing?
It processes IoT data near the source, reducing delay and improving speed.
What is the future of IoT and automation?
Fully autonomous, self-learning systems that manage environments with minimal human input.